
RPM maintains a database of installed packages, which enables powerful and fast queries. Metadata includes helper scripts, file attributes, and information about packages. An RPM package consists of an archive of files and metadata. RPM does provide you useful output, including a list of required packages. Still, it cannot manage dependency resolution like YUM. Using RPM, you can install, uninstall, and query individual software packages. RPM is a popular package management tool in Red Hat Enterprise Linux-based distros.
Also, here is a link to YUM documentation. For detailed option information, look at man yum and yum –help.

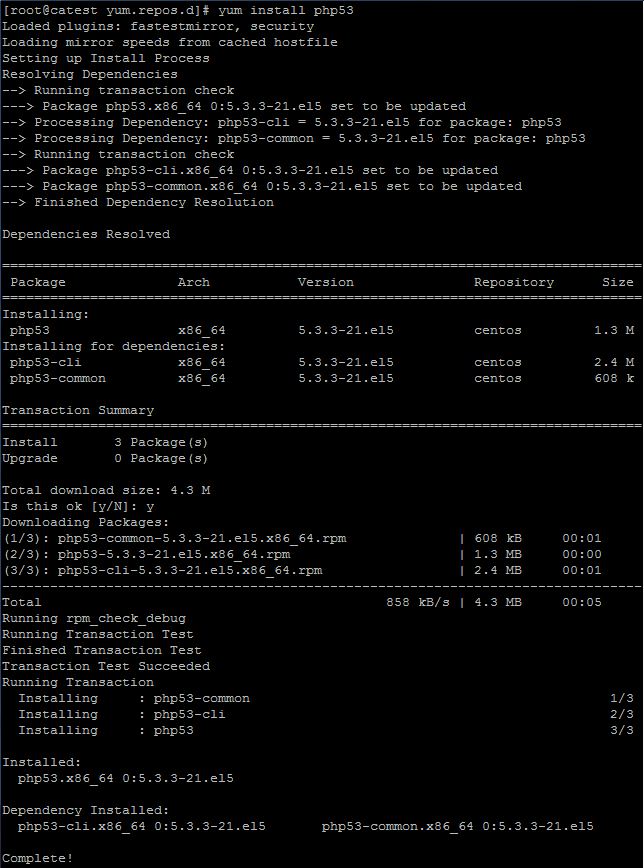
YUM provides many options for package management. Here is an example of undoing a transaction: yum history undo You can undo or redo certain transactions using the history command. This provides some useful information, like the date when the transaction happened and what command was run. The history option gives you an overview of what happened in past transactions. Includes packages that provide a fix for a security issue The following are commonly-used options with YUM: Options

Updates each package to the latest versionĭisplays what has happened in past transactions I've listed some commonly-used commands for YUM below: Command There are many options and commands available to use with YUM. It's easy to manage packages in Linux with YUM. You can learn more about adding repositories to your system from this article on how to add a YUM repo from Amy Marrich. The main configuration file for YUM is at /etc/yum.conf, and all the repos are at /etc/. YUM can manage packages from installed repositories in the system or from. YUM performs dependency resolution when installing, updating, and removing software packages. YUM is the primary package management tool for installing, updating, removing, and managing software packages in Red Hat Enterprise Linux. Red Hat-based distros use RPM (RPM Package Manager) and YUM/DNF (Yellow Dog Updater, Modified/Dandified YUM). Linux distros often use different package management tools. Package management is a method of installing, updating, removing, and keeping track of software updates from specific repositories (repos) in the Linux system. Here is how to get started with Linux package management in Linux Red Hat-based distributions (distros). Installing, patching, and removing software packages on Linux machines is one of the common tasks every sysadmin has to do.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
